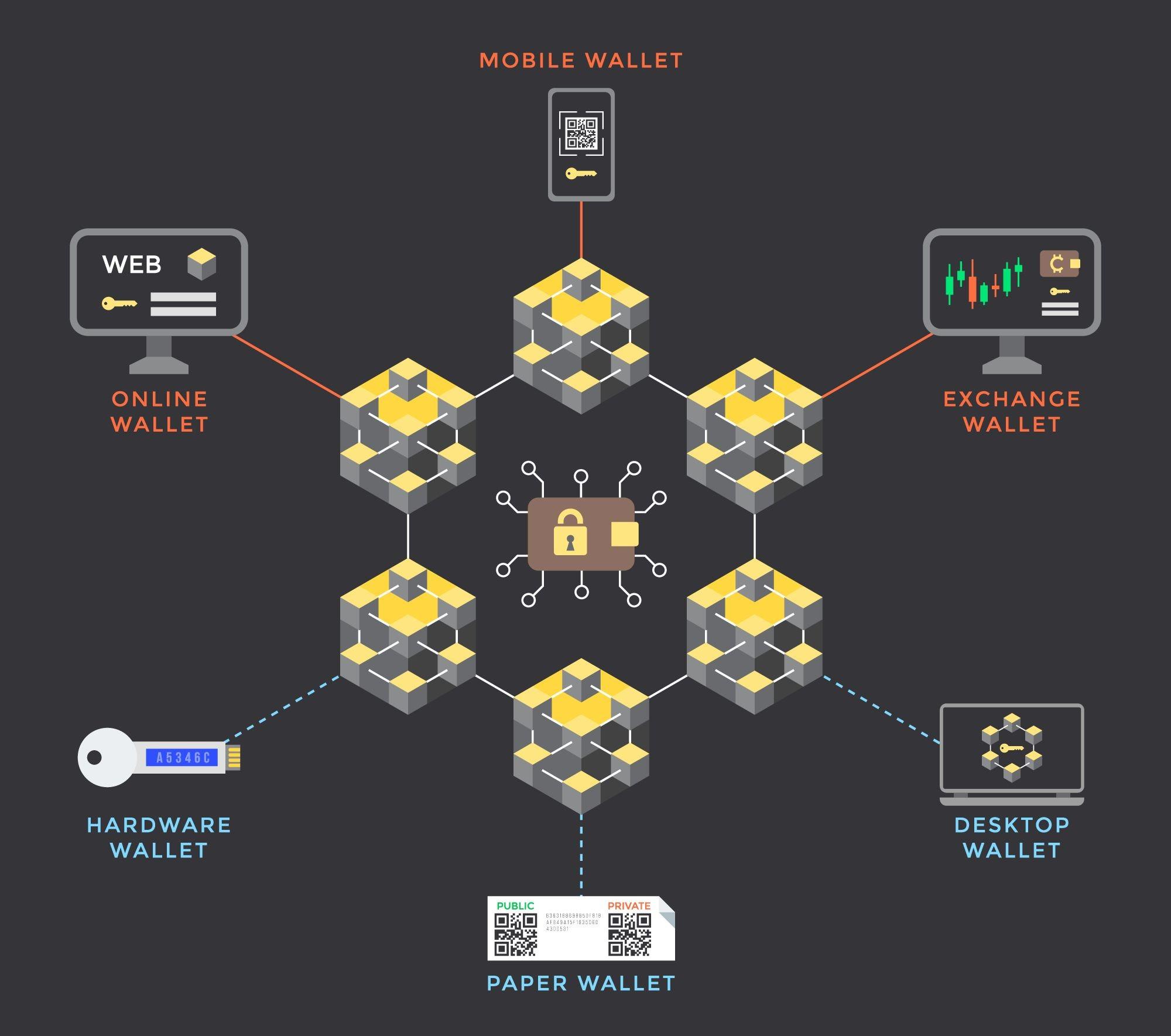
If you have ever dealt with digital assets such as cryptocurrencies, digital currencies, or NFTs, you are aware of the need for safe storage. You need a wallet/storage solution before you begin to make transactions, trade on a crypto exchange, or use blockchain applications.
If you are wondering how to store your digital currency, crypto assets, and tokens or how to assess the efficacy of different solutions, you are at the right place. There are two broad approaches to digital asset and crypto storage – custodial and non-custodial. Each approach has two types of wallets – Hot and cold. In this article, we will explore hot vs. cold wallets.
To learn about custodial vs. non-custodial services, check this article.
What Is A Crypto Wallet, And Why Do You Need Them?
Technically speaking, Crypto wallets don’t store your crypto or digital token like a normal pocket wallet holds your real-world currency. Instead, your assets live on the blockchain while your crypto wallet generates information, called keys, which you need in order to access your holdings or transact. A wallet provides you with two types of keys:
- Public key, which allows you to receive crypto or digital assets in your wallet.
- Private key, which allows you to authorize transactions.
It is critical to understand that the ownership of the private keys proves one’s ownership of the digital assets. If you lose your private keys, you lose access to your holding. There is a popular adage in the crypto world – “Not your keys, not your crypto.” That’s why it’s important to keep the keys safe and choose the right storage solution for your crypto assets.
Before we go further, let’s understand what “crypto keys” are and how the wallets generate and store them for safety.
What Are Crypto Keys?
As explained above, all crypto wallets generate a unique pair of public and private keys. There is a cryptographic link between the public key and the private key and hence, a pair is generated. Keep in mind that while a private key can generate a public key, vice-versa is not possible. As a result, if you lose your public key, you can recover it using your private key but it’s not feasible to derive a corresponding private key using just the public key. This feature is one of the lynchpins enabling secure blockchain transactions.
Private Keys: A private key is akin to your ATM PIN or unique signature on your bank cheque. This information must match in order for a transaction to be authorized. Therefore, private keys should only be known to the wallet/asset owner(s).
Public Keys: A public key is like your unique bank account number and can be freely shared. It allows you to receive or view cryptocurrency or digital assets. Anyone with your public key information will be able to view your assets on the chain.
How Does A Crypto Wallet Work?
The primary function of the crypto wallet is to securely store your public and private keys and provide digital signatures to authorize transactions on the blockchain. Some wallets enable owners to do more than just store keys, for instance, buying, selling, staking, or engaging with decentralized apps (DApps).
Every wallet is ascribed to a unique address. The wallet address is derived from your public key and is characteristically the last part of the public key. When you want to receive funds, you may share just the wallet address and not necessarily the public key to receive the digital asset or crypto in your holding.
Note: Public Key and Wallet Address are not the same thing.
Let get deeper
Fact 1: A Crypto wallet is essentially a computer application sitting on your device (PC, mobile/tablet, or dedicated hardware).
Fact 2: Cryptocurrencies, tokens, or other digital assets are not piled up together like the gold in your personal bank locker. Instead, the digital assets including your crypto are stored as bits of data scattered all over the database.
The wallet application locates all the bits mapped to your public address and presents the sum total for you in the app’s interface.
Wallets make it convenient to send and receive crypto. When you want to send crypto from your wallet, all you need to do is enter the recipient’s wallet address (or public key), input the amount to send, sign the transaction using your private key, and send it.
What Are the Types Crypto Wallets: Hot, Cold, and Paper Wallets
The most popular wallet types are Hot and Cold. But there is a third type called Paper wallet. Paper wallet was the earliest method of key storage and is not much in use today. However, we will describe all three in this article.
What Is A Hot Wallet?
Hot wallet refers to wallet software applications that are always connected to the internet and the blockchain infrastructure. This makes hot wallets swifter, convenient to use, and provide faster transaction speed. A typical hot wallet can be an on-prem software or a cloud-based app that allows interaction via a web application or the software on your mobile/tablet/PC.
Some prominent examples of hot wallets are Rainbow, MetaMask, and Coinbase Wallet.
While hot wallets are simple to get started (for beginners) and provide easy access as well as convenience, these wallets are also the most frequent target for hackers because they are always connected to the net. In other words, your public and private keys are always available online making this form of storage risky.
What makes hot wallets particularly vulnerable to hackers and attackers is the modus operandi of the hot wallet – all operations needed to accomplish a transaction are conducted from a singular online source. The wallet generates and stores private keys, digitally sign transactions using private keys, and broadcasts the signed transaction to the network. Once the transaction has been broadcast, bad actors crawling the networks may hack the private key used to sign the transaction.
PRO TIP: If deploying hot wallet services, look for security features such as 2-factor authentication, encrypting your wallet, updating the wallet software regularly, and keeping your wallet password safe.
Various hot wallets have been developed with varying usage intent and therefore, have distinct features. You might need more than one wallet to suit specific requirements. Some hot wallets are designed to interact with only specific types of blockchains. Also, some crypto exchanges accept transactions to and from only particular wallets. For instance, Metamask can be used for transacting within the Ethereum ecosystem while Coinbase Wallet can only be integrated with the Coinbase exchange. Some wallets are free while others charge a transaction fee. It is immensely important to recognize that different wallet service providers have vast variations in expertise, different levels of commitment to privacy and security, and varying priorities in mind when developing their wallets.
What Is A Cold Wallet?
Cold wallets are hardware devices (such as a USB key or other dedicated devices) that store your private keys offline. This makes cold storage much safer. In order to transact and access private keys, the user needs to connect the hardware to the cold wallet’s web/mobile application via USB stick, or Bluetooth. The wallet is then connected to the internet allowing the user to access the digital asset holdings. However, such exposure is for a brief period making cold wallets, a much safer option.
Importantly, the authorization process, which involves signing the transaction using private keys, is conducted in an offline environment by the cold wallet. The private key is not exposed to the internet at any stage of the process. It is this feature of the cold wallet that makes it more secure to operate vis-à-vis a hot wallet. Additionally, cold wallets are also password-protected.
Some popular hardware wallets include Ledger and Trezor.
PS: Propine does not recommend any brands, companies, or specific wallets. All mentions in this article are for academic and illustration purposes only.
Paper Wallet – Primitive Cold Wallet?
A paper wallet is the most rudimentary and archaic way of storing your keys. It is a physically printed-out document of your public and private keys. You can use a key generator (instead of a wallet) to generate your keys. The printed paper key pair comprises two alphanumeric text sequences or key strings, each for public key and private key as well as two corresponding QR codes for convenience of transaction. Since it is removed from the internet, it may be considered a type of cold storage.
While it seems a very secure method of storing your digital assets, danger looms large if you lose the printout or if it is damaged by water, torn, or rendered illegible. Besides, there are confidentiality threats associated with some types of web-based key generators.
Overall, paper wallets are an archaic method of key storage and are certainly not recommended for storing large amounts of digital assets.
How To Choose the Right Wallet?
The primary trade-off between hot and cold wallets encompasses choosing between convenience and security. Both have a reason to exist. We’ve summarized the main differences between hot and cold wallets in the table below:
Hot vs Cold Wallet: A Comparison
| Parameters | Hot Wallets | Cold Wallets |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Hot wallets live online. They are software, which can be accessed through a web browser or a mobile/tablet app. | Cold wallets are offline storage. They are hardware devices that are removed from the internet. |
| Security | Vulnerable to theft since they are connected to the internet | Relatively more protected from hacking and online attacks |
| Convenience | Very convenient. Very fast transaction speed | Add layers of additional steps to each transaction |
| Cost | Cheaper. Many hot wallets are free, but a few demand transaction fees. | Buying cold wallet hardware involves a one-time investment. |
| Private Keys Loss recourse | Many hot wallets offer “Secret Recovery Phrase” or “Seed Phrase” to gain access to the hot wallet that holds the private key. | Cold wallets also offer a recovery phrase mechanism to restore your hardware wallet configuration and your access to digital assets. |
| Usage Experience | Most hot wallets have an easy-to-grasp interface and are quick to learn | Cold wallets generally have a learning curve for most of non-native users. |
Which Wallet Type Is Best for You?
Internet is replete with news of colossal hacks of hot wallets. Exchanges, because of their centralized nature, are especially lucrative for hackers. According to Chainalysis, 2022 was the biggest year for crypto theft with $3.8bn stolen. In August 2022, over 8000 hot wallets comprising at least $5 million worth of SOL, SPL and other Solana-based tokens on the Solana chain were hacked. The saga goes on. Ultimately, selecting the right type of wallet will depend on several factors. Most users prefer a combination of hot and cold wallets based on needs and preferences. You may consider the following guidelines:
- If you are a frequent trader and accessibility is vital, consider researching hot wallets.
- If you wish to store a good lot of crypto or tokens and don’t mind sacrificing convenience for security, consider cold wallets.
Many users store a large part of their digital assets and crypto holding in cold wallets and a small amount for trading needs in hot wallets. They transfer from cold to hot wallets as required.
Another solution gaining acceptance among self-custody users is to use a secondary phone as a cold wallet. Such users hold some crypto for interim use in a secondary phone, which is always powered off. It is turned on only when the user needs to make a transaction. It connects to the primary phone, which holds the hot wallet, via Bluetooth or wifi and transfers funds. After the transaction is completed, the secondary phone is powered off again. Many users find this a more convenient method than investing in a cold wallet. However, the secondary phone solution is less secure than a hardware cold wallet solution.
Having said that, the best method of storing crypto depends on how you weigh speed, efficiency, and security risks. Each solution has its pros and cons, and it will eventually boil down to your personal assessment.
Bottom Line
As cryptocurrency becomes more mainstream and draws participation from non-native users, incidents of crypto fraud and crime are on the rise as well. Crypto wallets are evolving new technologies to adapt themselves to increasingly complex hacking attacks. There is no one size fits.
For users electing to self-custody their digital assets, the growing trend is to secure their holdings in hardware cold wallets. However, there are better and more secure solutions emerging such as multisig and multi-party computation. If you are an intuitional investor and want to learn more about these methods, reach out to us at contact@propine.com
Key Takeaways
- Crypto wallets help secure crypto keys. These wallets are of two types: Hot and Cold.
- Hot wallets are online wallets. Therefore, Hot wallets are relatively cheaper, faster to transact with, and more convenient to use.
- Cold wallets are hardware wallets that are offline. Relatively speaking, cold wallets offer better protection from hacking because they are not connected to the internet at all times.
- Most users prefer to use both types of wallets; cold ones for storage of large amounts and hot ones, holding small amounts, for frequent transactions.
- Crypto wallets are evolving as the threat of cybercrime and fraud in the crypto world is increasing. New security models are emerging every day.